

 Introduction
In the fast-paced world of logistics, efficiency and cost-effectiveness are crucial for businesses to stay competitive. While most people focus on traditional logistics—moving goods from manufacturers to consumers—reverse logistics plays an equally vital role in maintaining customer satisfaction and sustainability.
What is Reverse Logistics?
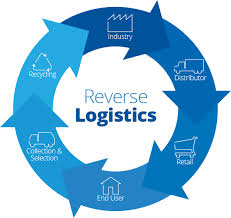
Reverse logistics refers to the process of moving goods from the consumer back to the manufacturer or retailer for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal. It includes activities like:
Product Returns: Managing customer returns due to defects, damages, or incorrect orders.
Recycling & Disposal: Ensuring used products are recycled properly or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner.
Refurbishment & Resale: Repairing or repackaging returned products for resale.
Asset Recovery: Recovering valuable components from used items for reuse.
Why is Reverse Logistics Important?
Cost Savings
Efficient reverse logistics can help businesses recover value from returned products, reducing waste and lowering operational costs.
Sustainability & Environmental Responsibility
Recycling and proper disposal of products help reduce environmental impact and comply with government regulations.
Customer Satisfaction & Loyalty
A seamless return process enhances customer trust, leading to higher retention rates and brand reputation.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries must follow strict guidelines for product disposal and recycling, making reverse logistics a legal necessity.
Challenges in Reverse Logistics
Despite its benefits, reverse logistics comes with challenges, such as:
High Processing Costs: Handling returns and refurbishments requires additional labor and resources.
Inventory Management Issues: Tracking returned goods and deciding their next steps can be complex.
Fraudulent Returns: Some customers exploit return policies, leading to financial losses.
How Companies Can Optimize Reverse Logistics
To overcome these challenges, businesses can:
Implement Smart Return Policies to reduce unnecessary returns.
Use Advanced Tracking Systems to monitor returned goods efficiently.
Partner with Recycling Firms to ensure eco-friendly disposal.
Automate Processes with AI and machine learning to improve efficiency.
Conclusion
Reverse logistics is no longer an afterthought—it’s a strategic advantage for companies looking to improve efficiency, cut costs, and enhance customer experience. By adopting innovative solutions, businesses can turn returns into revenue and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of logistics, efficiency and cost-effectiveness are crucial for businesses to stay competitive. While most people focus on traditional logistics—moving goods from manufacturers to consumers—reverse logistics plays an equally vital role in maintaining customer satisfaction and sustainability.
What is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to the process of moving goods from the consumer back to the manufacturer or retailer for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal. It includes activities like:
Product Returns: Managing customer returns due to defects, damages, or incorrect orders.
Recycling & Disposal: Ensuring used products are recycled properly or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner.
Refurbishment & Resale: Repairing or repackaging returned products for resale.
Asset Recovery: Recovering valuable components from used items for reuse.
Why is Reverse Logistics Important?
Cost Savings
Efficient reverse logistics can help businesses recover value from returned products, reducing waste and lowering operational costs.
Sustainability & Environmental Responsibility
Recycling and proper disposal of products help reduce environmental impact and comply with government regulations.
Customer Satisfaction & Loyalty
A seamless return process enhances customer trust, leading to higher retention rates and brand reputation.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries must follow strict guidelines for product disposal and recycling, making reverse logistics a legal necessity.
Challenges in Reverse Logistics
Despite its benefits, reverse logistics comes with challenges, such as:
High Processing Costs: Handling returns and refurbishments requires additional labor and resources.
Inventory Management Issues: Tracking returned goods and deciding their next steps can be complex.
Fraudulent Returns: Some customers exploit return policies, leading to financial losses.
How Companies Can Optimize Reverse Logistics
To overcome these challenges, businesses can:
Implement Smart Return Policies to reduce unnecessary returns.
Use Advanced Tracking Systems to monitor returned goods efficiently.
Partner with Recycling Firms to ensure eco-friendly disposal.
Automate Processes with AI and machine learning to improve efficiency.
Conclusion
Reverse logistics is no longer an afterthought—it’s a strategic advantage for companies looking to improve efficiency, cut costs, and enhance customer experience. By adopting innovative solutions, businesses can turn returns into revenue and contribute to a more sustainable future.